原本想用WebGL寫,不過語法不太熟悉,還是選用GLSL來實做Displacement Mapping。
語言:GLSL 模型:teapot 貼圖:color map和displacement map

- 左為color map,右為displacement map。
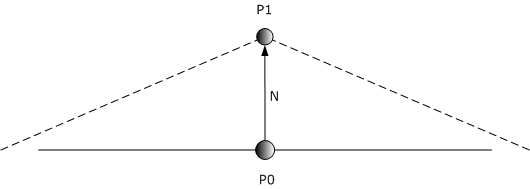 原理:
原理:
運算:P1 = P0 + (N * df * uf)
P0是原本頂點的位置、P1是經過displace後頂點的位置、N是model原本的法向量(displace後不變)、uf是自訂尺度、df = 0.30*dv.x + 0.59*dv.y + 0.11*dv.z,dv是displacement map的值,由R、G、B轉為灰階。

- 使用displacement map後diffuse的效果。

- 使用displacement map後specular的效果。

- 使用displacement map後color map的效果。

- 使用displacement map後color map * diffuse + specular的效果。

- 「不」使用displacement map後color map * diffuse + specular的效果。

- 使用displacement map後normal map的specular效果。

- 使用displacement map後color map * diffuse + normal map的specular效果。
在這裡我多加Bump Mapping的效果,來彌補就算Displacement Mapping能改變vertex的位置,但卻無法改變normal的缺點(就算shader會做內插,但內插結果往往跟理想的不一樣)。此外,Displacement Mapping暴露了一個缺點,就是當model的vertex不多時,得到的效果相當有限。
到這裡,vertex和pixel都有運算來改變model的特性,做到相當真實的效果,若還想要再真實一點,還可以加入陰影,用AO(Ambient Occlusion) map來做。
vertex shader程式碼:
varying vec3 vertex_position;
varying vec3 vertex_light_vector;
varying vec3 vertex_light_half_vector;
varying vec3 vertex_normal;
uniform sampler2D displacement_texture;
void main() {
vec4 newVertexPos;
vec4 dv;
float df;
gl_TexCoord[0].xy = gl_MultiTexCoord0.xy;
dv = texture2D( displacement_texture, gl_MultiTexCoord0.xy );
df = 0.30*dv.x + 0.59*dv.y + 0.11*dv.z;
newVertexPos = vec4(gl_Normal * df * 0.3, 0.0) + gl_Vertex;
gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix * newVertexPos;
// Calculate the normal value for this vertex, in world coordinates (multiply by gl_NormalMatrix)
vertex_normal = normalize(gl_NormalMatrix * gl_Normal);
vertex_position = vec3(gl_ModelViewMatrix * newVertexPos);
// Calculate the light position for this vertex
vec3 light_position = gl_LightSource[0].position.xyz;
vertex_light_vector = normalize(light_position.xyz - vertex_position.xyz);
// Calculate the light's half vector
vertex_light_half_vector = normalize(gl_LightSource[0].halfVector.xyz);
}
fragment shader程式碼:
varying vec3 vertex_position;
varying vec3 vertex_light_vector;
varying vec3 vertex_light_half_vector;
varying vec3 vertex_normal;
const vec3 eye_position = vec3(0.0,0.0,0.0);
uniform float updown, leftright, farnear;
uniform sampler2D color_texture;
uniform sampler2D normal_texture;
void main() {
// Extract the normal from the normal map
vec3 normal = normalize(texture2D(normal_texture, gl_TexCoord[0].st).rgb * 2.0 - 1.0);
// Determine where the light is positioned
vec3 light_pos = normalize(vec3(leftright, updown, farnear) + vertex_light_vector);
// Calculate the lighting diffuse value
float diffuse = max(dot(normal, light_pos), 0.0);
vec3 E = normalize(vec3(eye_position - vertex_position));
//vec3 R_d = normalize(vec3(reflect(-light_pos, vertex_normal)));
vec3 R_n = normalize(vec3(reflect(-light_pos, normal)));
// Defining The Material Colors
const vec4 AmbientColor = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
const vec4 DiffuseColor = vec4(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0);
const vec4 SpecularColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
// Calculate the ambient term
vec4 ambient_color = AmbientColor * gl_LightSource[0].ambient + gl_LightModel.ambient * gl_FrontMaterial.ambient;
// Calculate the diffuse term
vec4 diffuse_color = DiffuseColor * gl_LightSource[0].diffuse;
// Set the diffuse value (darkness). This is done with a dot product between the normal and the light
// and the maths behind it is explained in the maths section of the site.
float diffuse_value = max(dot(normalize(vertex_normal), vertex_light_vector), 0.0);
// Calculate the specular value
//vec4 specular_color_d = SpecularColor * gl_LightSource[0].specular * pow(max(dot(E, R_d), 0.0) , 100.0);
vec4 specular_color_n = SpecularColor * gl_LightSource[0].specular * pow(max(dot(E, R_n), 0.0) , 100.0);
vec3 color = diffuse_value * texture2D(color_texture, gl_TexCoord[0].st).rgb + specular_color_n;
// Set the output color of our current pixel
gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}
參考:Vertex Displacement Mapping using GLSL、Displacement Mapping。

Comments on: "[GLSL] 位移映射 (Displacement Mapping)" (5)
逍遙文大您好,
在看到了您對displacement mapping的描述後, 發現此方法可解決我目前的問題, 我現在正試著要透過WebGL將地球的表面造成有真實的高低起伏, 然後在顯示在網頁上, 而現在我本來就可以把png貼成一個解析度8192X4096的地球, 也有了灰階的地圖. 但問題就是如何實現, 我目前的想法是將原坐標加上調整後的值, 也就是: 調整後座標 = 法向量 X 灰階值 + 原座標; 我在這裡是否可以跟您請教, 相關知識的學習, 是否有推薦的外文書目或網站來學相關知識, 在這方面我實在不知道有什麼中文書有相關的, 還請賜教.
讚讚
嗨~你好!感謝你提出這麼詳細的問題~
這篇文章是我一年半之前研究GLSL的成果,現在忘了差不多XD~所以能回答你的問題可能不會很詳細,當然未來若有這類問題還是可以發問啦~
可以教你的是,GLSL的code可以直接用來寫WebGL,要注意的是「圖片座標」和「模型座標」的對應關係,應用上述的公式得出point新的位置,就能達到你要的效果。
讚讚
[…] 接著想製作真正凹凸不平的太空隕石,原理與效果可以參考我這篇:位移映射 (Displacement Mapping),Blender教學:法向量貼圖與太空隕石。 […]
讚讚
Vertex太少,寫個Geometry Shader內插增加數目即可,與Vertex Displacement相甫是為Tessellation。
讚讚
謝謝您的指教!這一點我也想過,可以用Geometry Shader來增加vertex數,在我整理的幾何著色器 (Geometry Shader) (https://cg2010studio.wordpress.com/2011/06/30/geometry-shader/) 有提到,OpenGL 3.2開始即有支援!只是我還不曉得要怎麼去寫它。
司馬仲軒您應該有Geometry Shader編程的經驗,可否提供給我做參考?我們可以互相交流。
讚讚