從上學期就看到此Phong Reflection Model的公式,
但也只知道表面而無法完全理解其內涵,
短短的一行等式中隱含著一個光的世界,
這時候我就把焦點放在【鏡射光(Specular)】上頭。
Phong Reflection Model

I = Ka*Ia + Kd*Id + Ks*Is
I: Illumination
分別為ambient、diffuse、specular的成份。
Ka,Kd為受到material color影響,Ks為受到light color影響。
Ka: ambient reflection常數
Kd: diffuse reflection 常數
Ks: specular reflection 常數
Ia is constant
Id = Ii * L · N
Is = Ii * (H · N) ^n或Is = Ii (V · R)^ n
Ii: Light的intensity。
n: shininess常數,n越大,則越平滑,且越像鏡面,也就聚光範圍越小。
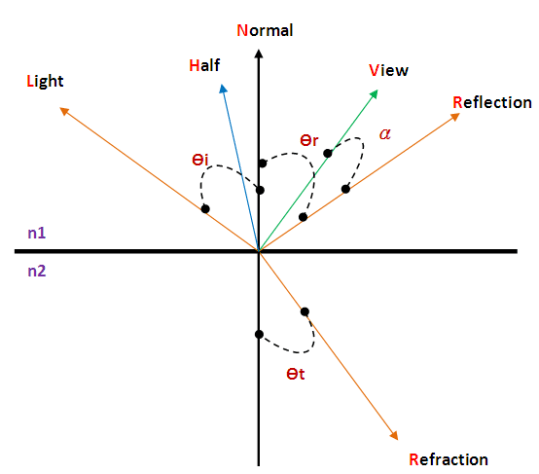
L · N、H · N、R · V 等內積結果為正時才有意義。
由於Phong的R計算量龐大,Blinn引進H = (L + V) / 2。
R跟V的夾角非常接近H跟N的夾角,H · N於是可以取代R · V,
由於R、V為單位向量,於是R · V等同於cosα。
若V越接近R,則H也會越接近N。(見圖好瞭解)
以下是實做【鏡射光(Specular)】的程式碼:
0// determine specular component
1if(prim->GetMaterial()->GetSpecular() > 0){
2 // point light source: sample once for specular highlight
3 vector3 V = a_Ray.GetDirection();
4 vector3 R = L – 2.0f * DOT(L, N) * N;
5 vector3 H = L + V;
6 NORMALIZE(H);
7 float dot = DOT(N, H);
8 if(dot > 0){
9 float spec = powf(dot, 1) * prim->GetMaterial()->GetSpecular();
10 // add specular component to ray color
11 a_Acc += spec * light->GetMaterial()->GetColor();
12 }
13}
注意紅色部份DOT(N, H)可取代DOT(V, R),
powf(dot, 1)中的數字有玄機,
(V · R)^ n一般範圍在[20, 100],
(N · H)^ n一般範圍在[0, 20],
光是看程式碼無法理解效果為何,
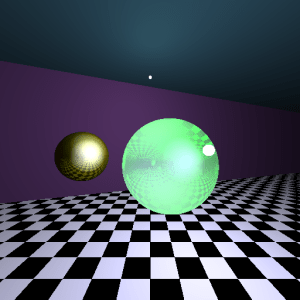
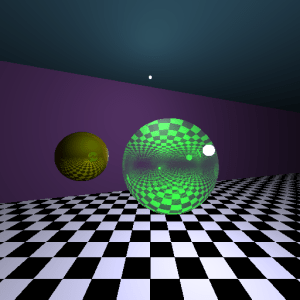
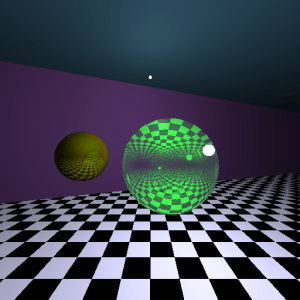
那麼請看以下我測試的成果:
有兩顆球(左邊有反射、右邊有反射和折射),
有兩個光源(上頭和右方)。
總述實驗結果:
N.H作用在Specular是呈現【物體形狀範圍】,
而V.R則是呈現【光源形狀範圍】。
兩者在n大的時候Highlight會消失,
這是由於cos介於[0, 1],
cos^n當n越大時~值會越小。
至於要用N.H或V.R就看你的需求,
若想要讓執行速度變快就使用前者,
至於效果就端視物體的特性來做選擇。




Comments on: "[C++] 鏡射光 (Specular)" (3)
[…] https://cg2010studio.wordpress.com/2011/03/27/specular/ […]
讚讚
[…] 3D HARDWARE-ACCELERATED LIGHTING MODELS、Illumination、鏡射光 (Specular)。 Share this:ShareEmailPrintFacebookTwitterLike this:LikeBe the first to like this […]
讚讚
[…] 參考:NeHe Diffuse Shader、我寫的Specular(鏡射光)。 […]
讚讚